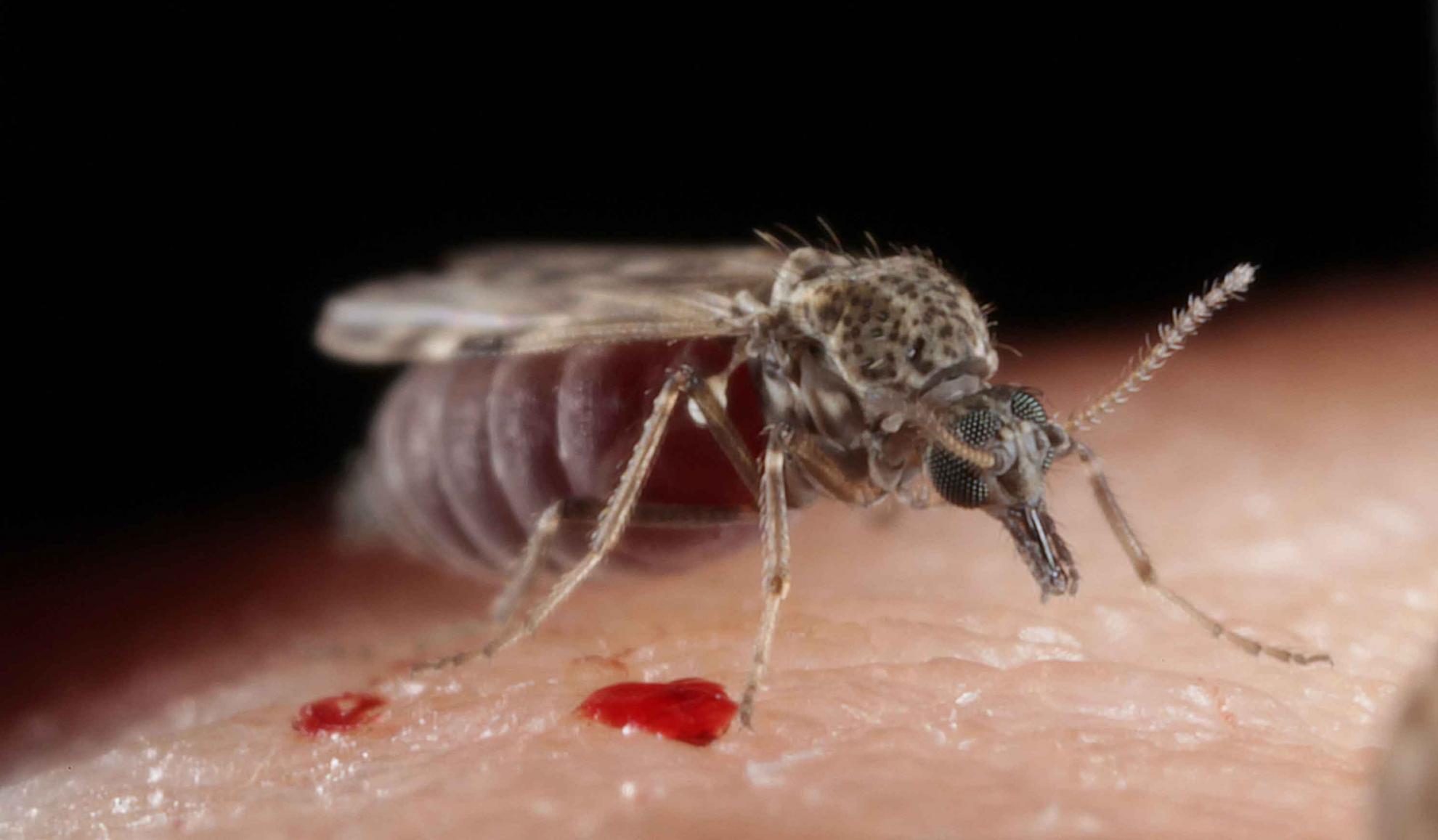
Visualisation of bluetongue virus in the salivary apparatus of Culicoides biting midges highlights the accessory glands as a primary arboviral infection site
Arthropods transmit a wide range of pathogens of importance for the global health of humans, animals, and plants. One of these arthropod vectors, Culicoides biting midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae), are the biological vectors of several human and animal pathogens, including economically important livestock viruses like bluetongue virus (BTV). Like other arthropods-borne viruses (arboviruses), Culicoides-borne viruses must reach and replicate in the salivary apparatus, from where they can be transmitted to susceptible hosts through the saliva during subsequent blood feeding. Despite the importance of the salivary gland apparatus for pathogen transmission to susceptible animals from the bite of infected Culicoides, these structures have received relatively little attention, perhaps due to the small size and fragility of these vectors.