Evidence of activation and suppression during the early immune response to foot-and-mouth disease virus
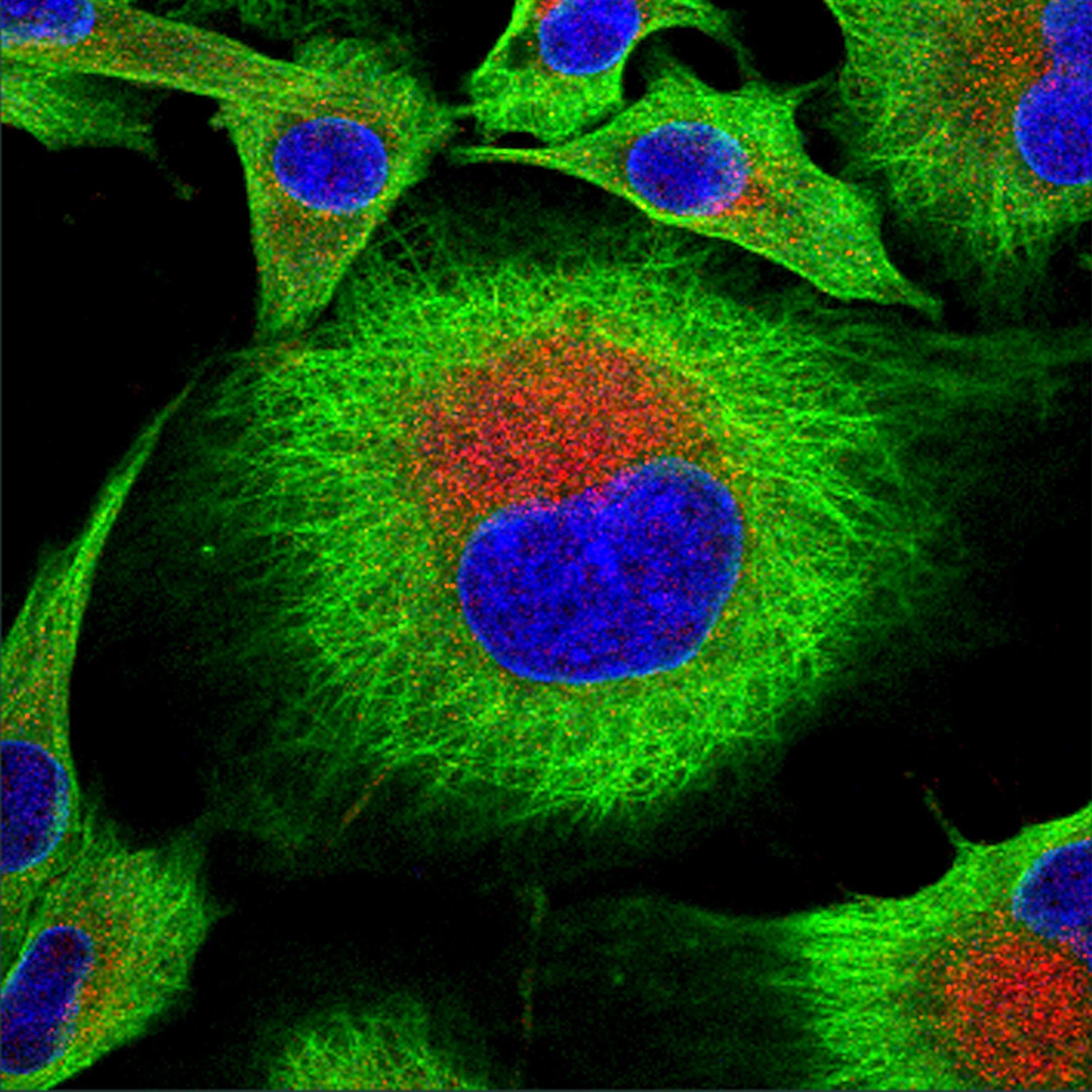
Foot-and-mouth disease virus causes a serious disease of livestock species, threatening free global trade and food security. The disease spreads rapidly between animals, and to ensure a window of opportunity for such spread, the virus has evolved multiple mechanisms to subvert the early immune response. The cycle of infection in the individual animal is very short, infection is initiated, disseminated throughout the body and infectious virus produced in <7 days. Foot-and-mouth disease virus has been shown to disrupt the innate response in vitro and also interacts directly with antigen-presenting cells and their precursors. This interaction results in suboptimal immune function, favouring viral replication and the delayed onset of specific adaptive T-cell responses. Detailed understanding of this cycle is crucial to effectively control disease in livestock populations. Knowledge-based vaccine design would specifically target and induce the immunological mechanisms of early protection and of robust memory induction. Specifically, information on the contribution of cytokines and interferon, innate immune cells as well as humoral and cellular immunity can be employed to design vaccines promoting such responses. Furthermore, understanding of viral escape mechanisms of immunity can be used to create attenuated viruses that could be used to develop novel vaccines and to study viral pathogenesis
Back to publications