The classical swine fever virus N-terminal protease N(pro) binds to cellular HAX-1
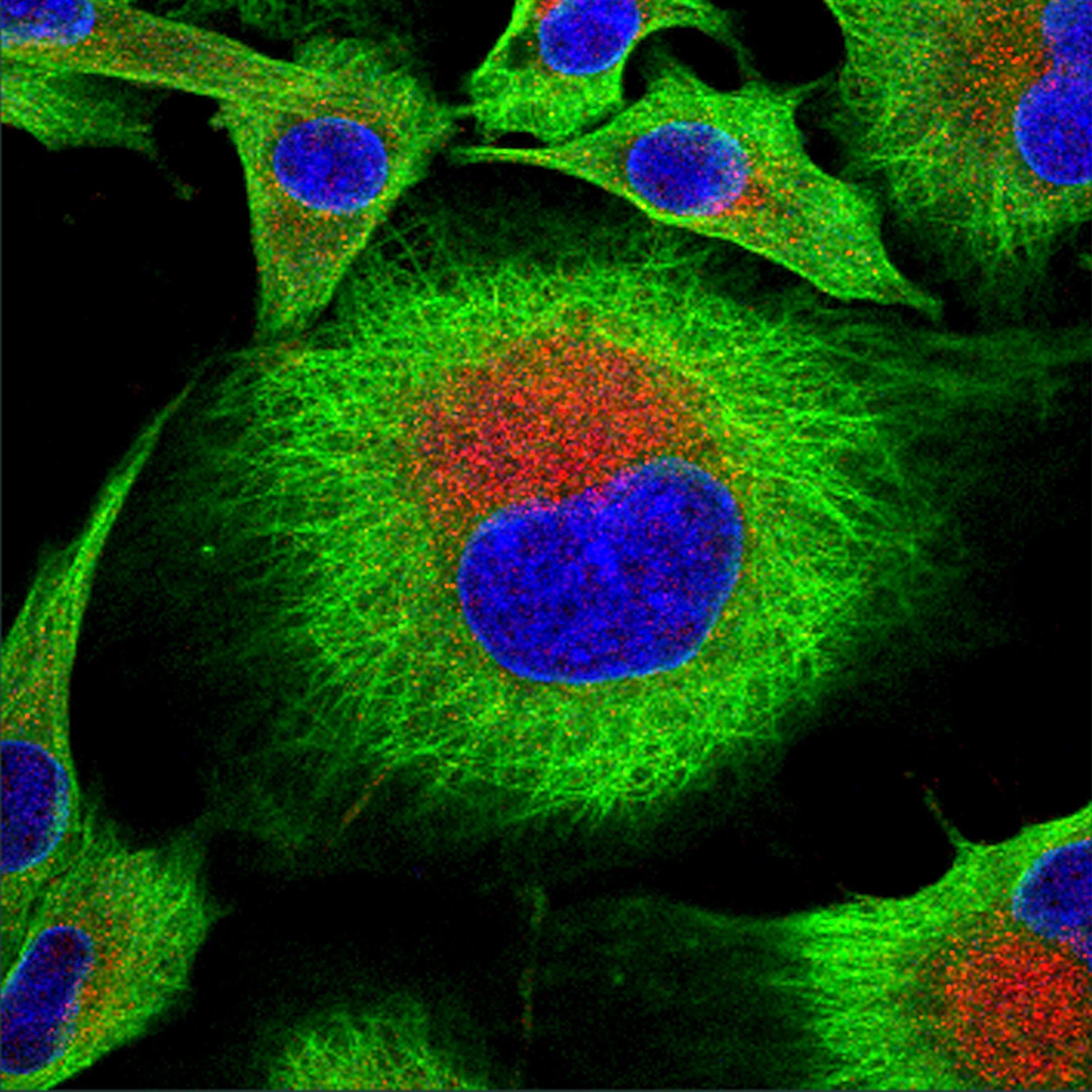
The positive-stranded RNA genome of classical swine fever virus (CSFV) encodes 12 known proteins. The first protein to be translated is the N-terminal protease (Npro). Npro helps evade the innate interferon response by targeting interferon regulatory factor-3 for proteasomal degradation and also participates in the evasion of dsRNA-induced apoptosis. To elucidate the mechanisms by which Npro functions, we performed a yeast two-hybrid screen in which the anti-apoptotic protein HAX-1 was identified. The NproHAX-1 interaction was confirmed using co-precipitation assays. A dramatic redistribution of both Npro and HAX-1 was observed in co-transfected cells, as well as in transfected cells infected with wild-type CSFV, but not in cells infected with an Npro-deleted CSFV strain.
Back to publications