African horse sickness virus: history, transmission, and current status
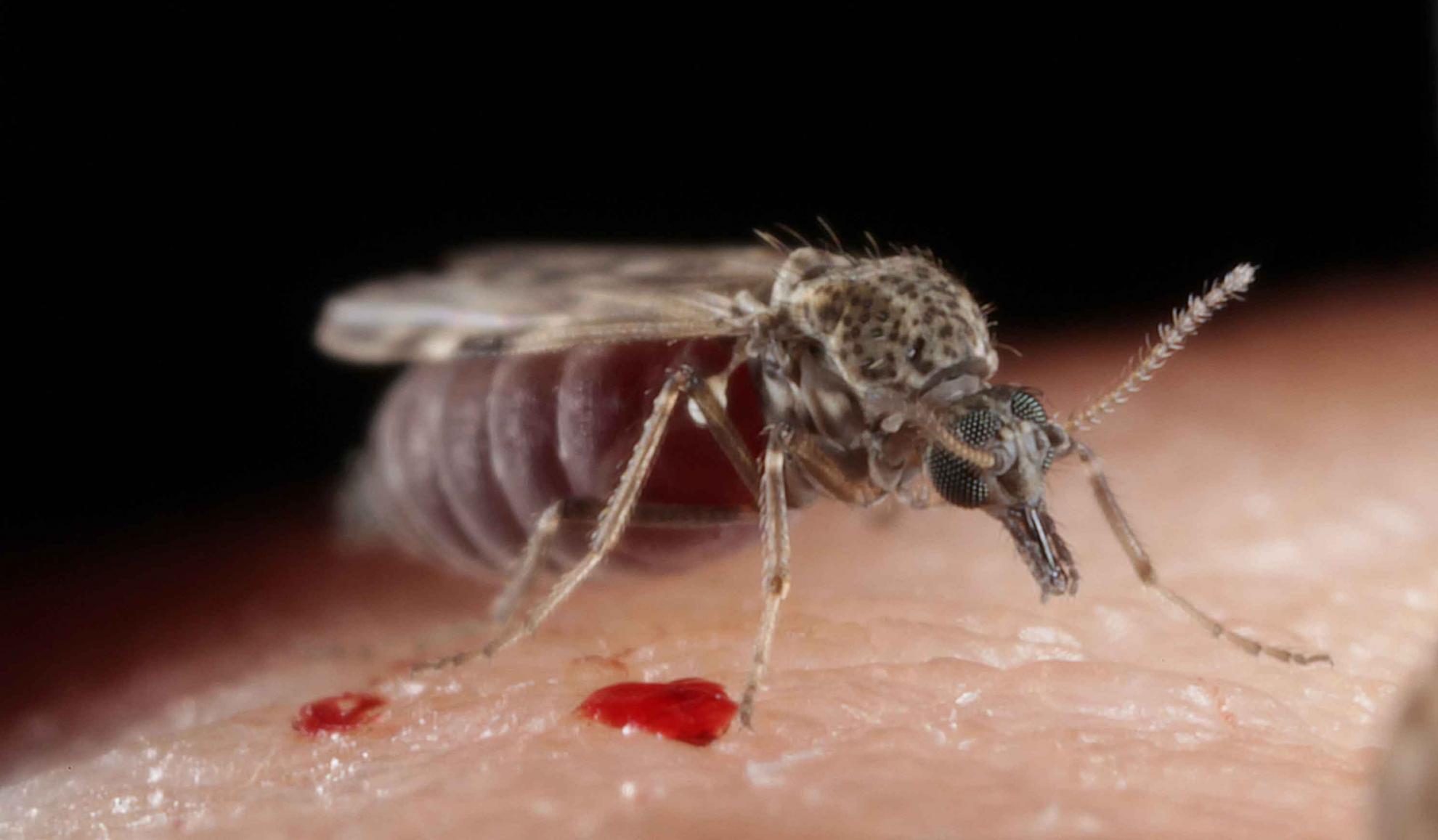
African horse sickness virus (AHSV) is a lethal arbovirus of equids that is transmitted between hosts primarily by biting midges of the genus Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). AHSV affects draft, thoroughbred, and companion horses and donkeys in Africa, Asia, and Europe. In this review, we examine the impact of AHSV critically and discuss entomological studies that have been conducted to improve understanding of its epidemiology and control. The transmission of AHSV remains a major research focus and we critically review studies that have implicated both Culicoides and other blood-feeding arthropods in this process. We explore AHSV both as an epidemic pathogen and within its endemic range as a barrier to development, an area of interest that has been underrepresented in studies of the virus to date. By discussing AHSV transmission in the African republics of South Africa and Senegal, we provide a more balanced view of the virus as a threat to equids in a diverse range of settings, thus leading to a discussion of key areas in which our knowledge of transmission could be improved. The use of entomological data to detect, predict and control AHSV is also examined, including reference to existing studies carried out during unprecedented outbreaks of bluetongue virus in Europe, an arbovirus of wild and domestic ruminants also transmitted by Culicoides.